The Next Generation of Service Assurance:
Your Network Is a Graph

Graph Analytics & AI Program Director
3 min read

Service complexity is exploding.
Communication Service Providers (CSPs) need a complete view of their network and its myriad interdependencies to drive real-time decisions and predict the impact of changes on the user experience. A native graph approach makes sense of complex networks and drives innovation, bringing new services from prototype to production.

In this series, we examine challenges in optimizing network services and how graph database technology overcomes them. Last week we covered trends driving major advances in service assurance.
This week, we’ll explain how graphs are ideal for modeling networks and show how relational database management systems (RDBMS) can’t keep pace with the interconnectedness and scale of today’s networks.
The Network Is a Graph
Telecommunications and enterprise networks are hyper-connected ecosystems of components, services and behaviors. And yet, critical information is often siloed: from physical items (such as end devices, routers, servers and applications), to activities (like calls, media and data) and customer information (rights and subscriptions).
A graph data model reveals cross-domain dependencies with a single unified view of the infrastructure and topology. Breaking down silos is at the heart of NGSA solutions.
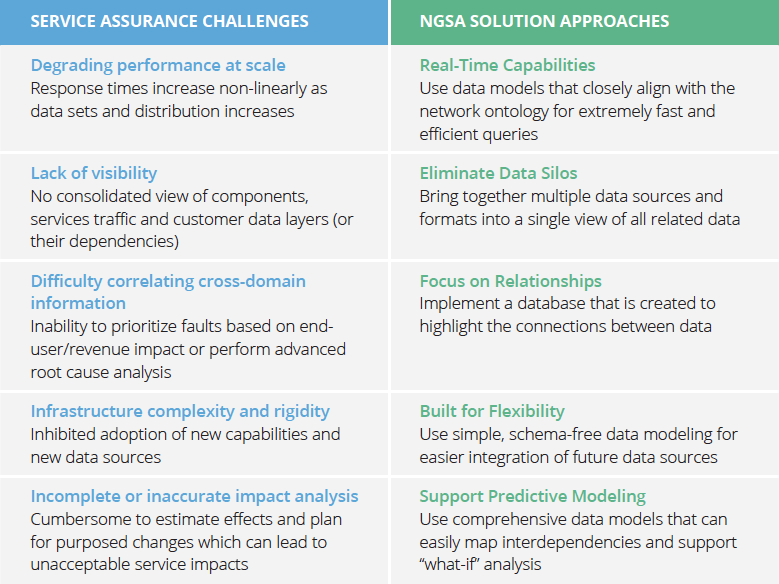
Advantages of a Native-Graph Approach
Neo4j, the world’s most relied upon graph platform, naturally captures relationships between data and therefore easily models network and service complexity. This emphasis on connections is unlike relational databases (RDBMS) that require careful schema development and complex joins to map multiple levels of relationships, which are then inflexible when adding new data.
Neo4j is specifically designed to store and process such multi-dimensional associations.
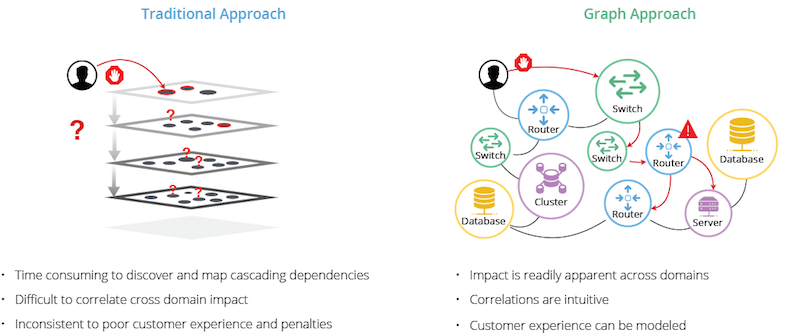
Service assurance requires performance and predictability, such as monitoring real-time end-user experience for automated responses. Because of its native graph storage, Neo4j thrives in querying such complexity at scale, easily outperforming RDBMS and other NoSQL data stores.
To deal with this type of processing, RDBMS approaches often resort to batch process or pre-computed schemes, which cannot deliver the results needed for immediate results.
Advantages for IT and Network Operators Using Neo4j
Network administrators, system administrators and application operators are able to readily recognize and understand the actual impact of maintenance activities and avoid surprising users downstream. They rapidly diagnose failures by correlating and tracing user complaints back to the application and infrastructure or cloud service where they are hosted.
Advantages for Telecom Operators Using Neo4j
Engineers and operators may create a singular view of operations across multiple networks at once, including cell towers, fiber lines, cable, customers and consumer subscribers or content providers. They improve customer experience by minimizing the impact of system maintenance or outages, such as being able to re-route services during an unexpected interruption, or identifying and preemptively upgrading vulnerable servers based on their maintenance history and availability.
Conclusion
As you can see, your network is a graph. Optimizing network services requires a real-time holistic view of network operations that only a graph database can provide.
Next week, we’ll explore how to rapidly build unique service assurance solutions – and how top telecom providers use Neo4j to differentiate their offerings.
Find out how top CSPs use connected data to capitalize on new market opportunities in this white paper, Optimize Network Services: Advanced Service Assurance with Neo4j. Click below to get your free copy.
Read the White Paper







