The ROI on Connected Data: How Connections Unlock Business Value [feat. eBay]

Product Team
7 min read

The value of data comes from an organization’s ability to understand it in relation to other data.
By itself, data offers finite value. When connected, data’s value is infinite.
Case in point: There’s a difference between knowing that a customer bought a child’s winter coat and knowing that a customer bought a child’s winter coat for the last three years, all in the color blue, in successive sizes.
Increasing data’s connectedness further increases its value through additional context. This is another demonstration of Metcalf’s Law of the Network: network value increases exponentially as you add users or nodes to the network.
In this series, we’ll examine how investments in connected data return dividends for your bottom line – and beyond. This week, we’ll take a look at how increasing data’s connectedness correspondingly increases its business value, including a case study taking a closer look at eBay.
What Is Connected Data?
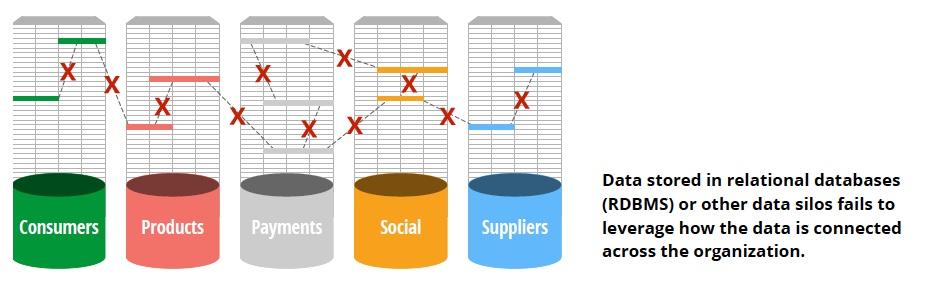
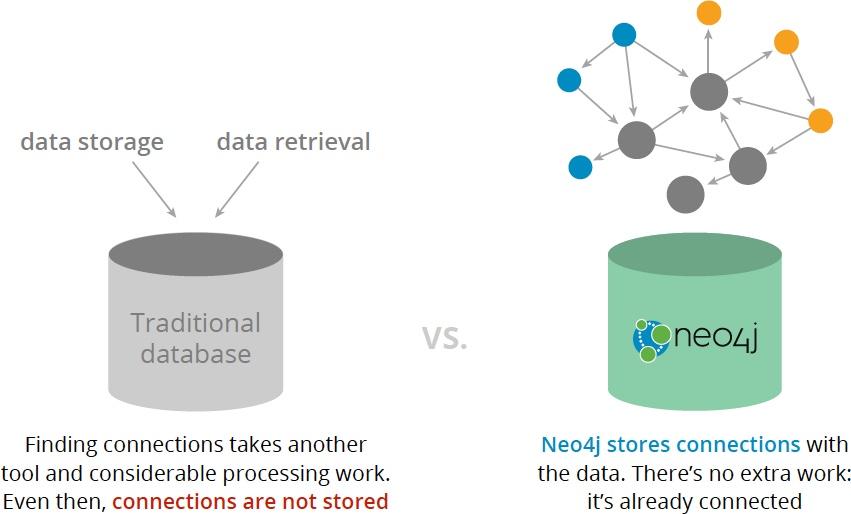
Connected data is the representation, usage and persistence of relationships between data elements. The key here is to maintain ongoing knowledge of the relationship and not simply instantiate it as might be done using a JOIN table in a relational database management system (RDBMS) (see below).
Data Lakes Store Data; They Don’t Connect It
Enticed by the promise of valuable business insights, companies have invested in big data technologies. But dumping data in a data lake doesn’t preserve nor reveal the relationships between data points. And JOIN tables only materialize a relationship when the query is run; relationship information is not a first-class entity in relational nor other types of databases.
Yet organizations express the need for connected data everywhere, especially when they are connecting people — like employees or customers — to products, business processes, networks, computers and Internet-enabled things (IoT).
Because relational databases don’t persist relationship information in storage or any other stage of their analytic exercises, finding connections requires an enormous amount of extra processing. And persisting these connections over their lifetime is next to impossible in an RDBMS. In a graph database like Neo4j, connections are stored as first-class entities with the data (see below).
Data, Data Everywhere, Nor any Drop to Drink
Like the ancient mariner at sea, organizations are surrounded by data but they’re limited in their ability to do anything with it.
They’ve collected all the data they could get their hands on in a desire to uncover the business insights that big data is known for. But despite having plenty of data, and data integration tools, organizations are failing to realize big data’s value.
That’s because the value isn’t in disparate data but in the relationships, or connections, between the data – and this information is not easily available.
Data doesn’t become connected by simply dumping it into a central data lake. Data becomes connected when you treat relationship information as a first-class entity — persisting it, assigning properties to it, and using it as a means to develop context for applications. Thus, it’s best to think of big data needing to be connected, not merely contained.
Case Study: The eBay App for Google Assistant
 eBay, Inc. is continually looking to improve the way shoppers find the perfect item since the typical search box experience regularly falls short in understanding and remembering what a shopper is truly seeking to find.
eBay, Inc. is continually looking to improve the way shoppers find the perfect item since the typical search box experience regularly falls short in understanding and remembering what a shopper is truly seeking to find.As an example, SVP & Chief Product Officer RJ Pittman considers the query: “My wife and I are going camping in Lake Tahoe next week, we need a tent.”
Most search engines would focus on the word “tent.” But the additional context regarding location, temperature, tent size, scenery, etc. is typically lost. Yet, this type of specific information is actually what informs many buying decisions. Relaying or maintaining this context (i.e., connected data) is often a burden left to the user and a new solution was needed to remove the hard work associated with shopping.
To remedy this issue, eBay used a Neo4j knowledge graph to power the eBay App for Google Assistant: a smart, personal shopping bot that converses with users via text, voice or photo search capabilities while parsing these conversations for meaning and context. This required a tool that could both efficiently navigate and leverage vast amounts of connected data.
To build the eBay App for Google Assistant, the engineering team needed a robust knowledge graph of connected data in addition to natural language understanding and artificial intelligence to store, remember and learn from past interactions with shoppers.
eBay chose Neo4j as the native graph database that holds the probabilistic models that aid understanding in the conversational shopping scenario. The Neo4j graph contains both the product catalog and the attributes of shopper interactions, creating and storing connections between both datasets as shoppers have more conversations.
When a shopper searches for “brown bags” for example, eBay App knows what details to ask about next, such as type, style, brand, budget or size. As it accumulates this information by traversing through the graph, the application is continuously checking inventory for the best match.
The eBay team expects to deploy the chatbot functions via plugins to Slack and Microsoft in the near future.
Conclusion
Without connected data, organizations lack key information that’s necessary to obtain a 360-degree view of the customer, build a complete network topology, deliver relevant recommendations in real time, or obtain the visibility required to prevent fraud.
The data landscape has grown, as has the number and types of connections upon which this data depends, making the need to surface connected data much more urgent (see below).
In the coming weeks, we’ll take a closer look at the power of connected data and the many use cases it enables. We’ll also see how connected data drives value and insights across industries from travel to telecom.
Click below to get your copy of The Return on Connected Data and learn how to create a sustainable competitive advantage with graph technology.
Read the White Paper