Neo4j Browser User Interface Guide
This article demonstrates how to use the Neo4j Browser for querying, visualization, and data interaction.
Please launch an AuraDB Instance or have Neo4j downloaded and installed. It also helps if you have read the section on graph databases.
Beginner
Neo4j Browser is an interactive cypher command shell that allows you to interact with your graph and visualize the information in it. Neo4j Browser is bundled with Neo4j and is available in all editions and versions of Neo4j.
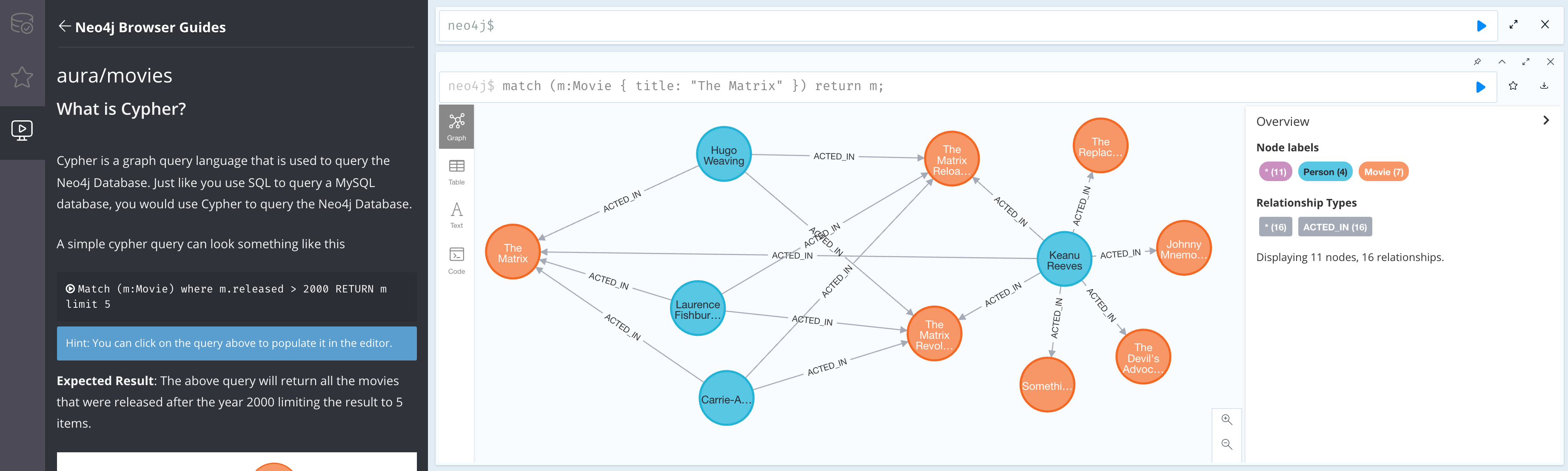
Launch Neo4j Browser
If you using AuraDB, go to the Aura Console, and find Neo4j Browser in the "Open" button.
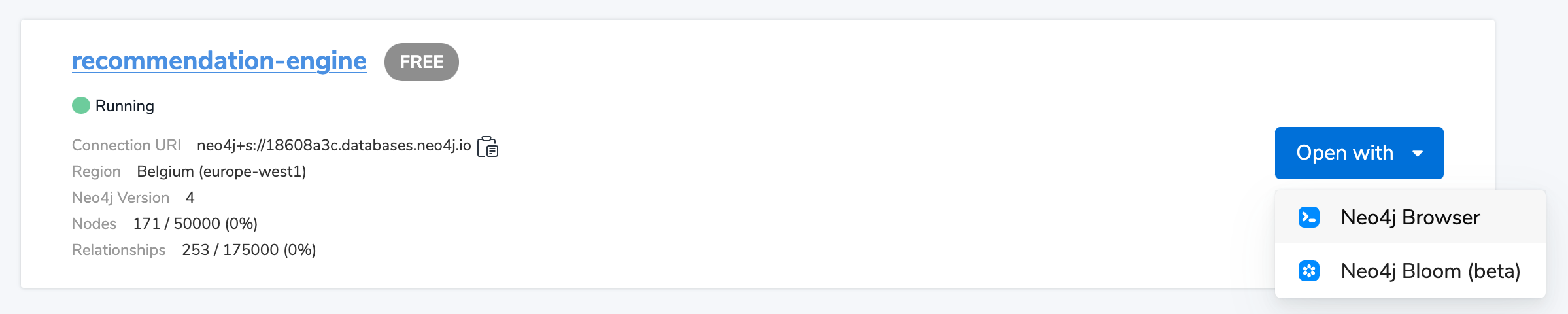
If you are using Neo4j Desktop, you can use the graph apps tab on the left hand side (which looks like four squares) to find Neo4j Browser, which will connect to any running database that you have.
If you are running Neo4j in another environment, Neo4j Browser is available via HTTP at http://localhost:7474 and HTTPS at https://localhost:7473,
substituting the right address for your environment.
Using Built-In Guides
Neo4j Browser contains built-in guides which introduce different concepts. Now that we can access the graph, we can use these guides to start working with data using Cypher.
To use one of these guides, just type the command (such as :play intro) into the command line on the right of Neo4j Browser and press Enter or click the play button (![]() ).
).
Title |
Description |
Command |
Intro |
A guided tour of Neo4j Browser |
|
Concepts |
Graph database basics |
|
Cypher |
Neo4j’s graph query language introduction |
|
The Movie Graph |
A mini graph model of connections between actors and movies |
|
The Northwind Database |
A classic use case of RDBMS to graph with import instructions and queries |
|
Custom Guides |
Use :play <url> to play a custom guide (custom guide documentation) |
|
The full list of available browser guides can be found here. You can also create your own custom browser guides to share learning with colleagues, students, and others in the community.
If you’d like to pin guides to the top so they do not get pushed down as you run additional queries, just use the pushpin button (![]() ) in Neo4j Browser.
) in Neo4j Browser.
Graph Metadata
In the left menu, the top icon is the database section (), where you can find the currently used node labels, relationship types, and property keys. Clicking on any one of those options runs a quick query to show you a sample of the graph with those elements.
Change Graph Appearance
Any query you run in Neo4j Browser will populate your results below the command line. You can switch between visual graph, table format, and ascii-table results with the icons on the left side of the result frame. You can also adjust by moving the view or dragging nodes to re-arrange them. To see more of the graph, click any empty spot and drag it.
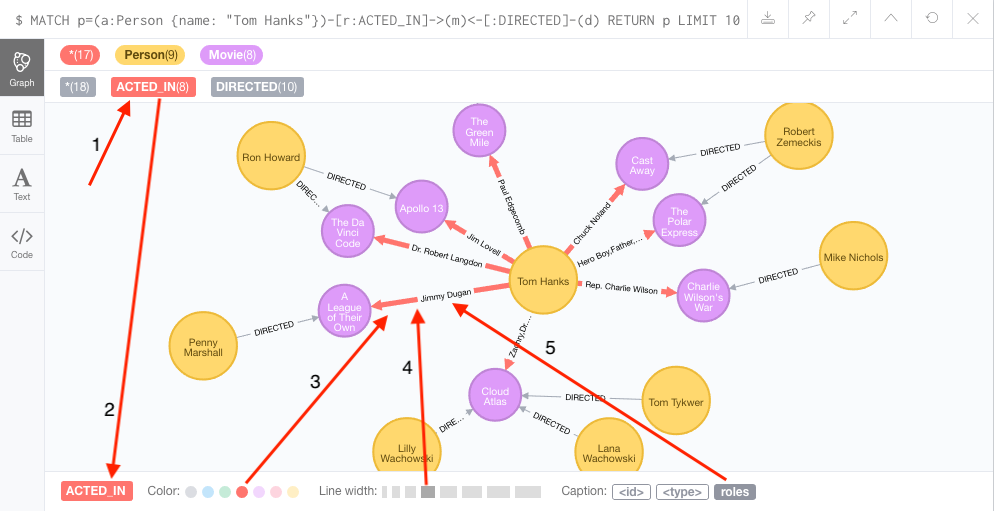
Nodes are assigned captions by the browser, which selects a property to use. These properties appear below the visualization when a node is selected. Larger property sets may be collapsed into a subset, but there is an option to expand them.
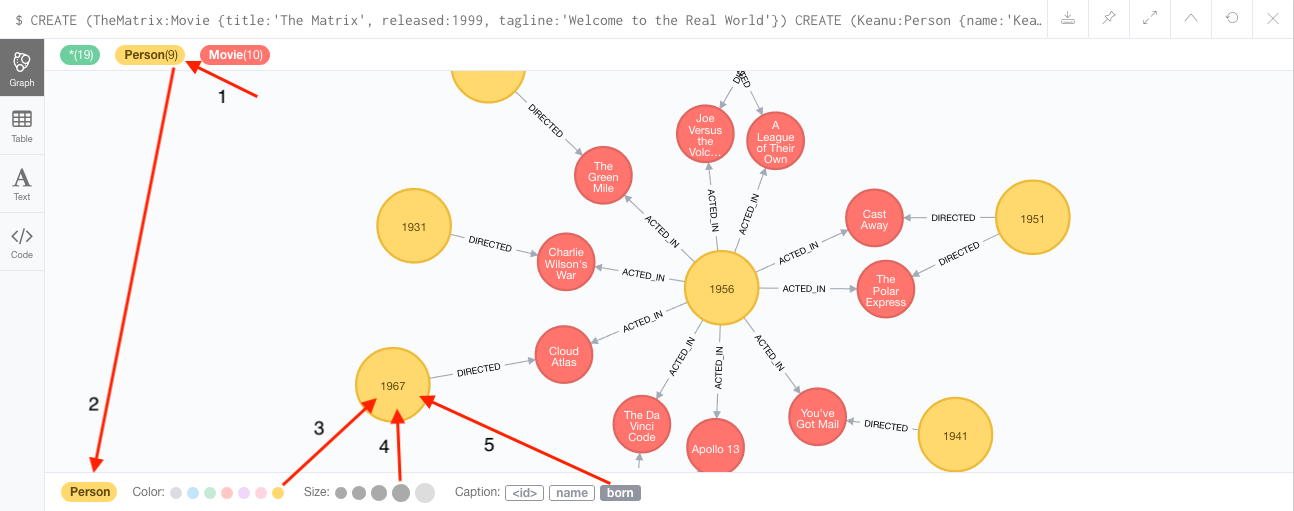
For example, if you click on one of the Movie nodes in the MovieGraph (:play movie graph), then you can see its properties below the graph visual.
The same applies for Actor nodes or the ACTED_IN relationships.
If you click on any label or relationship above the graph visualization, you can then choose its styling in the area below the graph.
Colors, sizes, and captions are selectable from there.
To see this for yourself, you can click on the Person label above the graph and change the color, size, and captions of all nodes labeled with Person.
The first image below shows changes to nodes labeled Person. The second image shows changes to relationships labeled ACTED_IN.
Commands and Keyboard Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
Help System |
|
Useful Commands |
|
Clear Frames |
|
Styling Popup & Reset |
|
Keyboard Help |
Ctrl+Enter or Cmd+Enter |
Execute Statement |
Ctrl+Up or Cmd+Up |
Previous Statement |
Shift+Enter |
Enter Multiline Mode |
/ |
Move Focus to Editor |
ESC |
Toggle Editor to Full Screen |
Query and Command-Line Tips
You can remove all accumulated output frames with :clear. The 'X' button at the top right of each pane removes that frame and aborts a (long-)running statement.
The maximum number of frames that are kept is configurable in the Browser Settings from the left-side menu.
If you want to review a past query, you can find the result pane and click the query above the graph visualisation to pull it back into the editor. The keyboard shortcuts listed above will help you work efficiently within the editor area.
You can also write and edit multi-line queries by switching to multi-line editing mode with Shift+Enter, then Enter will create newlines. You then need to run Ctrl+Enter or Cmd+Enter to run multi-line queries.
Ctrl+Up and Ctrl+Down (Mac users, use the Cmd key) allows you to navigate command history, and you can access all command history with :history.
The command history is persisted across Browser restarts.
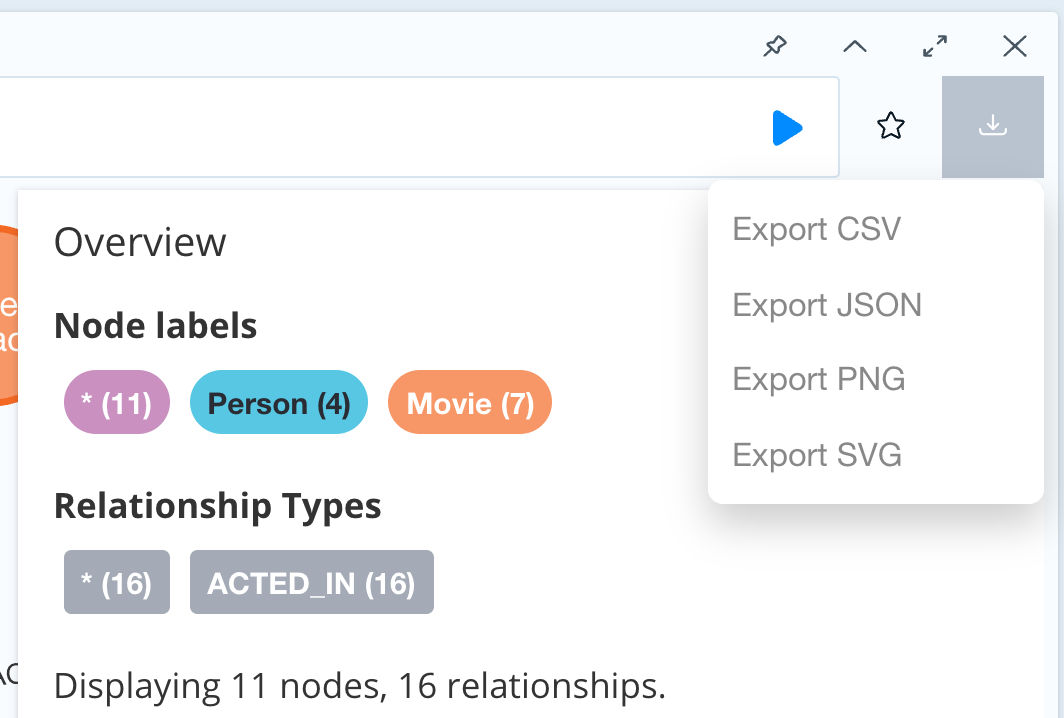
You can switch between Graph, Table, Text, and Code views to see the results in various formats by clicking the icons on the left of each pane.
|
Don’t worry if you don’t see any output. You might just be in Graph mode, but had your query return tabular/scalar data. To see the results, just switch the mode to the Table view. |
Query time is reported in the Table or Code views (don’t rely on that exact timing though), and it includes the latency and deserialization costs, not just the actual query execution time.
You can also export the results of queries as a CSV or JSON, and for the graph view, you may also export a PNG or SVG image, as shown below.
If you enter fullscreen mode of a graph visualization, you can zoom in and out. After a node is clicked, it gets a halo, where you can expand and remove nodes from the visualization. You can also turn previously dragged nodes loose again.
Setting Favorites
If you currently have an empty frame, you can display some nodes and relationships by using the Favorites () in the left-side menu.
Neo4j stores a few default favorites to get you started.
Just click on the Basic Queries, then choose Get Some Data and run the query.
This executes the statement MATCH (n) RETURN n limit 100, which fetches some nodes.
You can save your own queries as favorites by "starring" them. Just populate the Browser command line with the query you want to favorite, then click the Favorites () icon to the right of the command line. This will add the query to your Favorites list in the left-side menu. To run one of your Favorites, click on the left-side menu Favorites, choose the query, and run it.
To provide a title or helpful info, you can use a comment // comment above your query to provide a title.
The Favorites menu uses your comment as the query name.
Creating folders can help organize your favorites, and you can rearrange them by dragging or delete them if they are no longer useful.
Advanced Styling
For more advanced styling, you can bring up the style-viewer with :style and copy/paste the graph-style-sheet (GRASS) that is returned.
You can edit this stylesheet offline, save the file as a .grass file, and drag it back onto the drag-area of the viewer.
You can reset to the default styles with :style reset.
|
Within the GRASS file, you can change colors, fonts, sizes, outlines, and titles per node label and relationship type.
It is also possible to combine multiple properties into a caption with caption: '{name}, born in {born}';
Configuration
The defaults for all the settings can adjusted at any time by going to the configuration option on the left-side menu. Some possible config changes and views are listed below.
-
You can retrieve the current configuration with
:config. -
Individual settings are configured with the following defaults:
-
:config maxNeighbours:100- maxiumum number of neighbours for a node -
:config maxRows:100- maximum number of rows for the tabular result
-
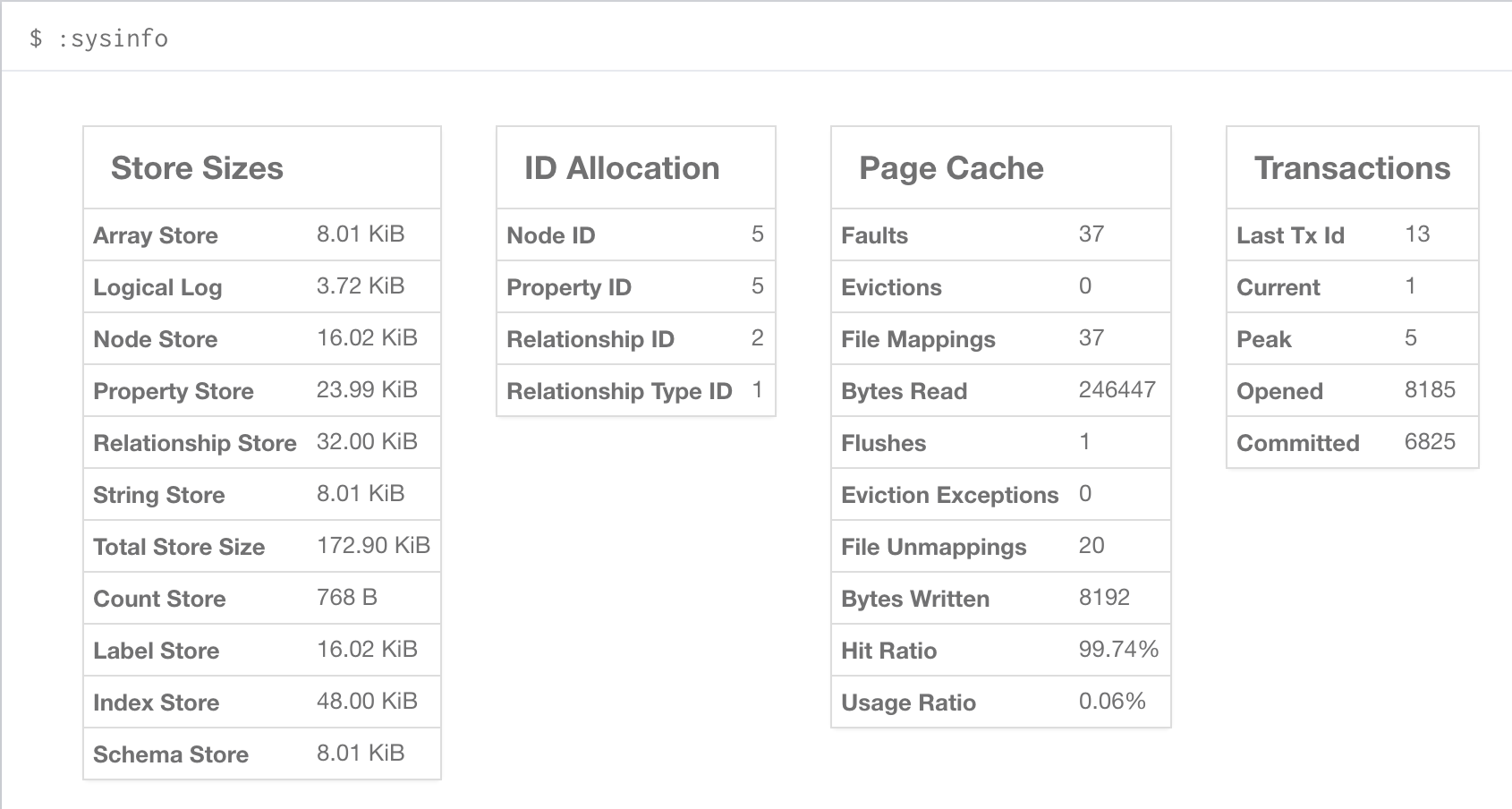
You can also see current stats on your database, such as store sizes, ID allocation, page cache, and transaction info.
To do this, just type the command :sysinfo on the command line.
Executing REST requests
You can also execute REST requests with Neo4j Browser. The command syntax is :COMMAND /a/path {"some":"data"}.
The available commands are :GET, :POST, :PUT and :DELETE.
A simple query like :GET /db/data/ inspects the available endpoints of the database, with the returned results formatted in JSON.
Then, you can retrieve all labels in the database with :GET /db/data/labels.
To execute a Cypher statement, you post to the transaction Cypher endpoint like this:
:POST /db/data/transaction/commit {"statements":[
{"statement":"MATCH (m:Movie) WHERE m.title={title} RETURN m.title, m.released, labels(m)",
"parameters":{"title":"Cloud Atlas"}}]}There are endless possibilities to send and retrieve data using REST. In a later guide, you can create an application to interact with Neo4j and use REST endpoints for interaction between you and the database. See the Language Guides section for more information.
Was this page helpful?